What is WebSocket?
-
Unlike HTTP, which works on a request-response model, WebSocket creates a persistent connection.
-
Once the connection is established, both the client and server can send messages to each other at any time, without waiting for a request.
This makes WebSocket ideal for real-time applications where data needs to be updated frequently or instantly, like chat apps, online games, or stock price trackers.
WebSocket vs. HTTP: When to Use Each
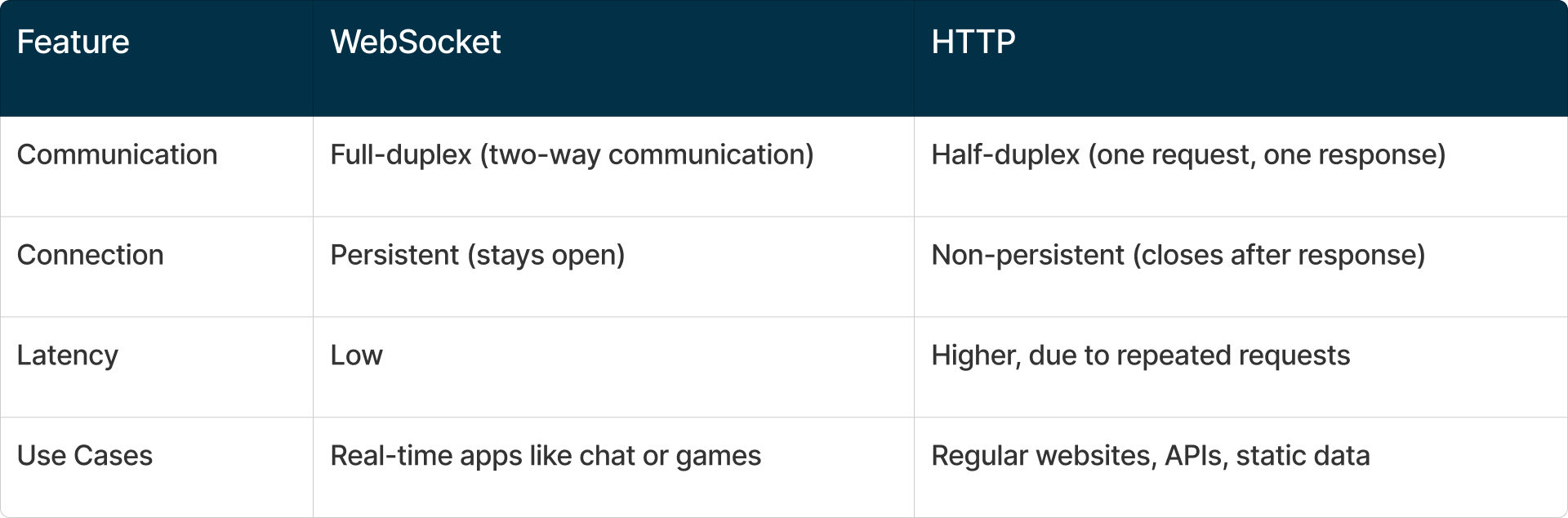
When to Use WebSocket in .NET:
-
Real-time data streaming: For live dashboards, stock tickers, or real-time notifications.
-
Interactive apps: Chat apps, collaborative tools, or online games.
- High-frequency data updates: Apps requiring constant data flow, like IoT systems.
When to Stick to HTTP in .NET:
-
Static or periodic data: Websites or APIs that don’t need frequent updates.
-
Simpler architecture: Apps with low interaction or data flow needs.
Why Use WebSocket in .NET Applications?
-
Efficient Use of Resources: Instead of making multiple HTTP requests, WebSocket uses a single connection, reducing server load and saving bandwidth.
-
Low Latency: Data is sent and received quickly, making it perfect for apps where speed is crucial.
- Improved User Experience: Enables live updates, instant notifications, and smooth interactions.
Advanced WebSocket Features in .NET Core
1. Middleware Support
.NET Core provides built-in middleware to integrate WebSocket into your app quickly.
app.UseWebSockets();
app.Use(async (context, next) => {
if (context.Request.Path == "/ws") {
if (context.WebSockets.IsWebSocketRequest) {
var webSocket = await context.WebSockets.AcceptWebSocketAsync();
await HandleWebSocketCommunication(webSocket);
}
} else {
await next();
}
});
2. Streaming Support
3. Authentication
4. Scalability with SignalR
-
Automatic reconnection.
-
Broadcasting messages to multiple users.
- Pub/sub architecture for large-scale apps.
How to Implement WebSocket in .NET
Step 1: Set Up WebSocket Middleware
Enable WebSocket in your ASP.NET Core app.
app.UseWebSockets();
Step 2: Create WebSocket Handlers
Write a handler to manage WebSocket connections and process incoming/outgoing messages.
private async Task HandleWebSocketCommunication(WebSocket webSocket) {
var buffer = new byte[1024 * 4];
WebSocketReceiveResult result;
do {
result = await webSocket.ReceiveAsync(new ArraySegment<byte>(buffer), CancellationToken.None);
var message = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer, 0, result.Count);
await webSocket.SendAsync(new ArraySegment<byte>(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes($"Echo: {message}")), WebSocketMessageType.Text, true, CancellationToken.None);
} while (!result.CloseStatus.HasValue);
await webSocket.CloseAsync(result.CloseStatus.Value, result.CloseStatusDescription, CancellationToken.None);
}
Step 3: Connect with a WebSocket Client
Use JavaScript on the client side to establish a WebSocket connection.
const socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:5000/ws");
socket.onopen = () => {
console.log("Connected");
socket.send("Hello Server!");
};
socket.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log("Message from server: ", event.data);
};
Best Practices for WebSocket in .NET
1. Error Handling
-
Add retry mechanisms for failed connections.
-
Handle timeouts to ensure the app remains stable.
2. Data Security
3. Load Balancing
4. Testing
5. Scalability
Use SignalR for large apps that need features like reconnection and message broadcasting.
Benefits of WebSocket in .NET Applications
-
Real-Time Updates: Push live data to users instantly, improving app responsiveness.
-
Scalability: Handle thousands of connections efficiently, thanks to .NET’s robust framework.
- Cross-Platform Support: Deploy your WebSocket-enabled app on Windows, Linux, or macOS using .NET Core.


Dipak Pakhale
A skilled .Net Full Stack Developer with 8+ years of experience. Proficient in Asp.Net, MVC, .Net Core, Blazor, C#, SQL, Angular, Reactjs, and NodeJs. Dedicated to simplifying complex projects with expertise and innovation.
Reply